THC Vape Laws and Regulations: An Authoritative Guide
Understanding the legal landscape surrounding THC vape products is essential for consumers, businesses, and regulators alike. As the market for cannabis-derived vaping products continues to evolve, the interplay between federal and state laws creates a complex regulatory framework that can be challenging to navigate. This article provides an in‑depth look at THC vape laws and regulations, covering federal and state statutes, key legal issues, regulatory bodies, case studies, market impacts, and future trends.
Introduction to THC Vape Laws and Regulations
The rapid growth of the cannabis vaping market has brought THC vape laws and regulations into sharp focus. These legal standards determine how THC vape pens are manufactured, sold, and consumed, influencing both public health and industry practices. THC vape laws encompass everything from federal restrictions under the Controlled Substances Act to state-specific rules regarding age limits, possession, and distribution. As cannabis legalization expands across the United States—with 24 states legalizing recreational use and 39 allowing medical use—conflicts often arise between federal prohibitions and state-level liberalization.
Recreationally Legal States (24 States)
In these states both recreational and medical cannabis are legal. Licensed dispensaries sell a wide range of products—including THC vape pens—that are subject to rigorous testing, labeling, and age‐restriction rules.
- Alaska
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Illinois
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nevada
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- Ohio
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
In these states, a consumer seeking a THC vape can purchase products from state‐licensed cannabis dispensaries that meet testing and packaging standards.
Medical-Only, CBD/Low-THC, or Fully Prohibited States (26 States)
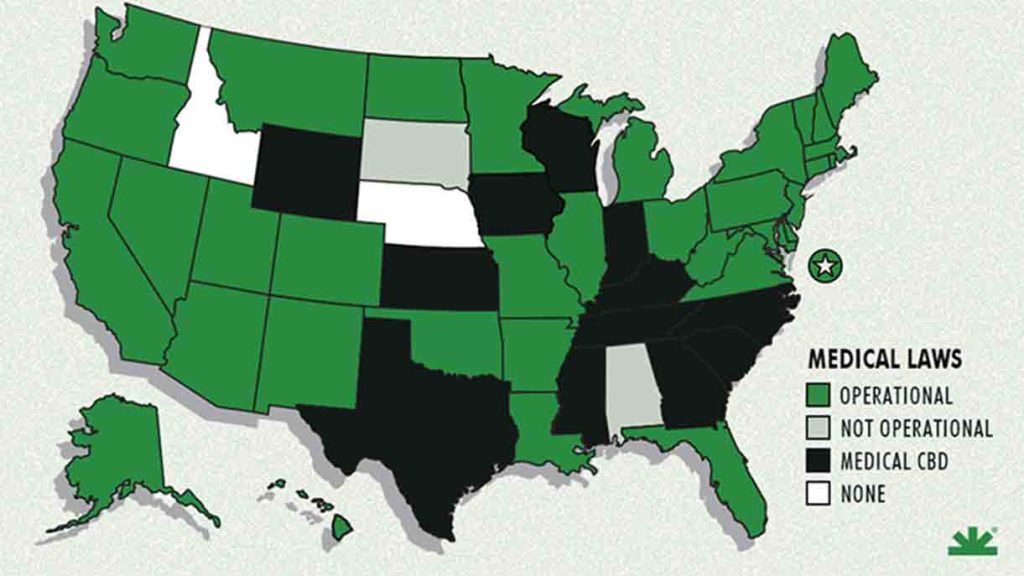
These states either permit cannabis only for medical purposes (and often then only in the form of low-THC or CBD oil) or maintain a near-total prohibition on cannabis products with intoxicating levels of THC. In such states, THC vape pens—if they deliver a psychoactive dose—are not legally available.
- Alabama – Medical program exists, but only low‐THC (typically CBD) products are permitted.
- Arkansas – Medical use is allowed; recreational products (including high‐THC vapes) are not legal.
- Florida – Operates a medical cannabis program only; recreational THC products are not available.
- Georgia – Only low‐THC (CBD oil–only) programs are in place.
- Hawaii – Medical cannabis is legal, but recreational products (including high‐THC vapes) remain prohibited.
- Idaho – Cannabis remains fully illegal; only non‐intoxicating CBD is permitted.
- Indiana – Only very low‐THC (CBD oil–only) products are legally available for specific medical conditions.
- Iowa – Allows only CBD/low‐THC medical products.
- Kansas – No legal cannabis program beyond CBD products with no detectable THC.
- Kentucky – Has a limited medical program (CBD oil only); recreational use is not legal.
- Louisiana – Medical cannabis is legal, but the market is limited to non‐recreational formulations.
- Mississippi – Medical use is allowed; recreational high‐THC products are not available.
- Nebraska – Cannabis is fully illegal except for permitted CBD with zero or trace THC.
- New Hampshire – Only medical cannabis is allowed; recreational products (and thus THC vape pens) are not legal.
- North Carolina – Cannabis remains illegal aside from non‐intoxicating CBD oil.
- North Dakota – Operates a medical cannabis program only.
- Oklahoma – Only a medical cannabis program exists.
- Pennsylvania – Medical use is legal; recreational sales (including THC vape pens) are not allowed.
- South Carolina – Cannabis is fully illegal except for approved CBD products.
- South Dakota – Has a medical-only program; recreational cannabis is not legal.
- Tennessee – Permits only CBD oil (with very low THC levels) for limited medical purposes.
- Texas – Only allows low‐THC (CBD oil–only) products under a restrictive medical program.
- Utah – Has a medical program only; recreational high‐THC products are not available.
- West Virginia – Medical cannabis is legal, but recreational use is prohibited.
- Wisconsin – Only CBD oil is allowed; full-spectrum cannabis products remain illegal.
- Wyoming – Cannabis is fully illegal except for strictly defined CBD products.
In these states, consumers generally cannot purchase legally a THC vape product that delivers a psychoactive “high” because the law limits products to non-intoxicating formulations.
While federal law still classifies cannabis as a Schedule I substance, the 2018 Farm Bill created a loophole for hemp-derived products containing less than 0.3% delta‑9 THC. This distinction has paved the way for a burgeoning market in hemp‑derived THC vape products; however, it also creates uncertainty regarding product safety and legal compliance. In this article, we explore the nuances of federal versus state regulations, examine key legal issues such as possession limits and concentration restrictions, and analyze how regulatory agencies enforce these laws.
Staying informed about these evolving regulations is crucial not only for legal compliance but also for protecting consumer health and ensuring industry sustainability. With authoritative data from sources like the California Department of Cannabis Control and the FDA, this guide aims to provide clarity on an often-confusing legal terrain.
Federal and State THC Vape Laws and Regulations
Federal Regulations:
At the federal level, cannabis remains classified as a Schedule I substance under the Controlled Substances Act. However, the 2018 Agriculture Improvement Act—commonly known as the Farm Bill—established a critical exception by legalizing industrial hemp, defined as cannabis with less than 0.3% delta‑9 THC by dry weight. This legislative nuance means that many hemp-derived THC vape products fall into a legal gray area. Despite this, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) continues to enforce federal laws that broadly criminalize cannabis, creating tension between federal mandates and state policies.
State-Specific Regulations:
State THC vape regulations vary significantly. For example, California has one of the most robust regulatory frameworks in the nation, with comprehensive licensing, testing, and age verification requirements designed to ensure consumer safety and product quality. In contrast, states like Texas maintain stricter enforcement of federal cannabis laws, often resulting in severe penalties for possession—even of hemp-derived products if they exceed the permitted THC concentration.
States set their own limits on THC vape possession and sales, and these limits may include requirements for product labeling, packaging, and even tracking systems to monitor distribution. Age restrictions are another common element, with most states mandating that purchasers be 21 years or older. Such state-level measures aim to minimize youth access and safeguard public health while allowing regulated, legal markets to flourish.
Balancing Federal and State Laws:
The discrepancy between federal cannabis law and state legalization efforts creates legal ambiguities that have been subject to recent court challenges. For instance, cases examining whether certain THC vape products fall under hemp regulations or constitute illicit cannabis have highlighted the complexities inherent in a dual regulatory system. This evolving legal landscape means that businesses and consumers must remain vigilant and well-informed about the laws in their specific jurisdictions.
In summary, while federal law provides a broad prohibition on cannabis, state regulations have carved out exceptions for hemp-derived products—resulting in a patchwork of legal standards across the country. For more detailed state-by-state insights, consult the State Marijuana Laws Overview on NORML.
Key Legal Issues in THC Vape Regulations
Possession and Distribution Limits:
One of the central issues in THC vape laws is the regulation of possession and distribution limits. Many states impose strict limits on the amount of THC-containing vape products an individual can legally possess or purchase. These limits are designed to curb potential misuse and diversion into the black market, which can undermine public health and safety. For example, certain states enforce fines or even felony charges for possession exceeding legally defined thresholds.
THC Concentration and Product Standards:
A crucial point of legal contention is the permissible concentration of THC in vape products. The 2018 Farm Bill clearly defines hemp as containing less than 0.3% delta‑9 THC, but creative chemistry has allowed manufacturers to produce products containing other cannabinoids (such as delta‑8 THC and THC‑O) that still deliver intoxicating effects. The legal status of these derivatives has led to significant debate and court rulings. Recent cases, influenced by decisions that have undermined deference to agency interpretations, have forced courts to reexamine whether products like THC‑O should be regulated as synthetic cannabinoids—a category that is federally prohibited.
Enforcement Challenges and Penalties:
Enforcement of THC vape regulations varies widely. While some states have implemented rigorous testing, tracking, and licensing systems, others struggle with enforcement due to resource constraints. Penalties for non-compliance can range from monetary fines to severe criminal charges, including felony convictions. This uneven enforcement environment can lead to significant market disruptions, as businesses that fail to meet regulatory standards may face shutdowns or legal actions.
Recent Court Rulings and Ambiguities:
Recent legal cases have highlighted the ambiguity of THC vape regulations. For instance, court decisions influenced by challenges to the Chevron deference doctrine have resulted in mixed rulings about what constitutes a legal hemp product. Such cases underscore the ongoing legal battles and the uncertainty that surrounds THC vape enforcement. These issues directly impact both consumers and businesses, making it imperative to stay updated on the latest legal developments.
By addressing these legal issues, regulators aim to strike a balance between enabling a legal market for hemp-derived THC vape products and preventing abuse and health risks. Consumers and businesses must navigate these challenges carefully, keeping abreast of both federal and state enforcement practices.
Regulatory Bodies and Their Roles
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA):
The DEA is primarily responsible for enforcing federal drug laws, including those that pertain to cannabis and its derivatives. Although the 2018 Farm Bill has opened a legal pathway for hemp-derived products, the DEA continues to maintain a firm stance on cannabis as a Schedule I substance. This enforcement creates a challenging dynamic for companies manufacturing or selling THC vape products, as they must ensure that their products comply with both federal limits and state regulations.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA):
The FDA plays a critical role in overseeing the safety, labeling, and marketing of cannabis-derived products, including THC vape products. Recent guidance documents from the FDA have focused on ensuring that products are free of harmful contaminants and that claims made by manufacturers are substantiated by scientific evidence. The FDA’s oversight is especially important for products that blur the line between dietary supplements and drugs, with implications for both consumer safety and market legitimacy. For further details, refer to the FDA Regulation of Cannabis and Cannabis-Derived Products.
State Cannabis Control Boards:
At the state level, agencies such as the California Department of Cannabis Control enforce regulations that govern the licensing, testing, and sale of THC vape products. These bodies are tasked with ensuring compliance with state-specific laws, which may include rigorous testing protocols, strict labeling requirements, and age verification systems. Their efforts are pivotal in maintaining product quality and protecting consumers, particularly in states with well-developed recreational and medical cannabis markets.
Collaborative Enforcement:
Often, enforcement involves collaboration between federal, state, and local agencies. This multi‑layered approach is necessary due to the overlapping jurisdictions and the inherent complexities of cannabis regulation. The combined efforts of the DEA, FDA, and state regulatory bodies work together to curb the sale of illicit products while allowing a regulated market for compliant hemp-derived THC vape products.
By understanding the roles and responsibilities of these regulatory bodies, businesses and consumers can better navigate the legal framework and ensure that they remain in compliance with both federal and state laws.
Case Studies and Recent Developments
California’s Regulatory Model:
California offers one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks for THC vape products. The state requires rigorous testing for contaminants and mandates strict labeling requirements to ensure that consumers are informed about THC concentrations. Recent regulatory updates have focused on addressing the influx of hemp-derived vape products that skirt federal limits while still delivering psychoactive effects. The California Cannabis Laws and Regulations provide a benchmark for best practices in licensing, enforcement, and consumer protection.
Texas’ Enforcement Challenges:
In contrast, Texas remains one of the more conservative states regarding cannabis regulation. Enforcement in Texas tends to be stricter, with significant penalties for possession or distribution of THC vape products that exceed legal thresholds. Businesses operating in Texas often face uncertainty due to the state’s limited legal market and the risk of federal intervention. This has led to increased instances of products being seized and heavy fines imposed on violators, creating a chilling effect on legal commerce in the region.
Recent Court Decisions and Legal Ambiguities:
Recent legal battles have further highlighted the complexities of THC vape regulation. For example, court cases questioning the legal status of synthetic cannabinoids—such as THC‑O—demonstrate how judicial interpretations can diverge from both agency guidance and legislative intent. Decisions like those emerging from challenges to federal deference rules have underscored the need for clearer legal standards. These cases serve as cautionary tales for businesses, emphasizing the importance of staying compliant with both state and evolving federal guidelines.
Market Impact and Industry Response:
The legal ambiguity has had tangible effects on the industry. Some companies have adapted by reformulating products to ensure THC concentrations remain below the federally mandated thresholds. Others have shifted to more transparent practices, investing in third‑party testing and quality assurance to build consumer trust. Despite these challenges, the market for THC vape products continues to grow, driven by consumer demand for legal, high‑quality cannabis vaping options.
These case studies underscore the significant variations in THC vape enforcement across states and highlight the ongoing evolution of regulatory standards. Keeping up-to-date with these developments is essential for both industry stakeholders and consumers alike.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
Consumer Considerations:
For consumers, understanding THC vape laws is vital for making informed decisions about product safety and legal compliance. Strict age restrictions—typically set at 21 years or older—are enforced across most states to protect minors. Consumers are encouraged to purchase from licensed dispensaries where products undergo rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. This not only helps mitigate health risks but also reduces the likelihood of encountering illicit or mislabeled products.
Business Challenges:
Businesses operating in the THC vape market face significant regulatory hurdles. Compliance with diverse state regulations can result in high operating costs, particularly for testing, licensing, and quality control. In states with stringent enforcement, non-compliance can lead to heavy fines, product seizures, or even felony charges. Moreover, the ongoing legal ambiguities—especially concerning hemp-derived products—create additional uncertainty that can stifle innovation and market growth.
Market Dynamics:
The tension between legal hemp products and illicit alternatives has also spurred shifts in consumer behavior, with some turning to the black market for cheaper options. This trend undermines state efforts to regulate the market and protect public health. As a result, both regulators and industry leaders emphasize the importance of transparency, robust testing, and consumer education to ensure that legal products remain competitive and safe.
Understanding these market impacts is crucial for anyone involved in the THC vape industry or considering purchasing these products.
FAQs on THC Vape Laws and Regulations
Q: Are THC vape pens legal at the federal level?
A: Under federal law, cannabis remains a Schedule I substance; however, the 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp-derived products with less than 0.3% delta‑9 THC, creating a legal pathway for certain THC vape products.
Q: What are the age restrictions for purchasing THC vape products?
A: Most states require buyers to be at least 21 years old to purchase THC vape products.
Q: How do state laws differ regarding THC vape regulations?
A: Some states impose strict possession limits, mandatory licensing, and robust testing protocols, while others adopt a more lenient approach. These differences can affect both the availability and quality of legal products.
Q: What penalties apply for violating THC vape laws?
A: Penalties vary by state and may range from fines and probation to felony charges, depending on the quantity and nature of the violation.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Navigating the legal landscape for THC vape products requires an understanding of the complex interplay between federal prohibitions and state‑specific regulations. This guide has outlined the key legal issues, regulatory bodies, and recent developments impacting the market—from federal statutes like the Controlled Substances Act and the 2018 Farm Bill to state‑level enforcement in places like California and Texas. As the industry evolves, consumers and businesses alike must remain informed and vigilant to ensure compliance and protect public health.







[…] long can THC from a vape be detected in […]
[…] more severe cause of nausea associated with THC vapes is Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome (CHS), a rare condition experienced by chronic cannabis users. […]